Most people immediately think of hearing aids when it comes to treating hearing loss. They’re the most effective solution and nearly 29 million Americans could benefit from using them, but they are not the only option.
From everyday amplification tools to specialized support systems, understanding these options can help you make informed decisions that align with your needs and lifestyle.
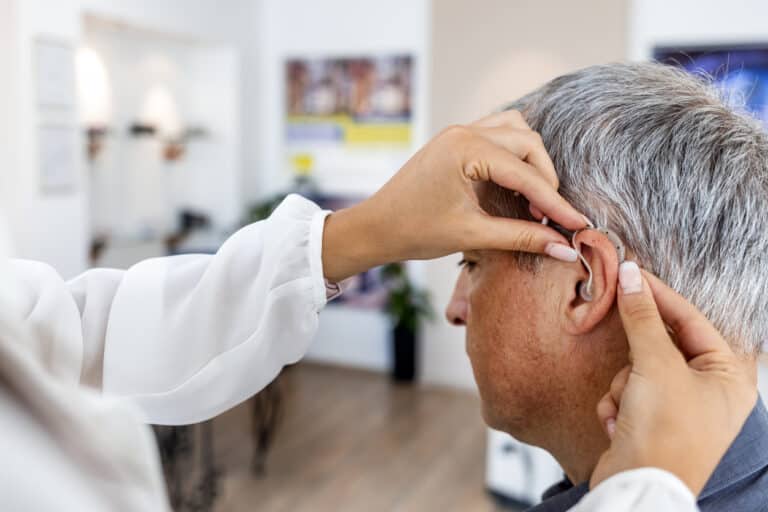
Hearing Aids
Hearing aids are compact electronic devices that sit either in or behind the ear and are designed to make sounds louder and clearer.
- Bluetooth® connectivity for audio streaming
- Rechargeable battery systems
- Noise-canceling capabilities
- Directional microphones for better sound focus
With multiple styles and fits available, hearing aids can be tailored to fit your hearing profile and personal preferences.
Assistive Listening Devices
While hearing aids work well in many situations, assistive listening devices provide added support in environments where background noise or distance may be a challenge.
Common types of assistive listening devices include:
- Personal amplifiers: These handheld tools pick up nearby sound and amplify it directly to your ears, ideal for small group conversations.
- FM systems: Often used in educational or group settings, FM systems transmit a speaker’s voice to a listener’s device using radio signals.
- Induction loop systems: These systems use magnetic signals to send sound directly to telecoil (T-coil) equipped hearing aids, frequently used in public venues like theaters or houses of worship.
- Bluetooth® streamers: These devices allow wireless audio streaming from phones, tablets or computers to your hearing aid or cochlear implant.
These tools can significantly improve hearing in settings that might otherwise be overwhelming.
Captioning and Visual Alert Systems
Not all solutions for hearing loss rely on sound. Some devices focus on translating or signaling information through text, light or vibration.
Useful non-audio hearing aids include:
- Captioned phones: These show real-time transcriptions of phone conversations so you can read as you listen.
- Visual alerts: These systems use blinking lights or vibrations to notify you of doorbells, phone calls, or smoke alarms.
- TV captioning: Options include real-time subtitles or enhanced dialogue modes to make television easier to follow.
These devices can improve communication and safety, especially in the home.
Cochlear Implants and Bone-Anchored Devices
When traditional hearing aids don’t provide enough support, especially in cases of severe or profound hearing loss, other medical solutions may be recommended.
These include:
- Cochlear implants: Surgically placed devices that bypass damaged inner ear components to directly stimulate the auditory nerve.
- Bone-anchored hearing systems (BAHS): These use bone conduction to send sound vibrations to the inner ear, ideal for conductive or one-sided hearing loss.
Both solutions require evaluation and recommendation by a hearing healthcare specialist.
Finding the right device depends on several factors, such as:
- The type and degree of hearing loss you have
- Your daily environments and communication needs
- Your comfort with different kinds of technology
A consultation with a hearing specialist can help guide you to the best combination of tools and support strategies for your hearing journey.
If you’re interested in learning more about hearing aids or other hearing support options, contact PDX ENT today to schedule a personalized hearing evaluation.